Masterkey mode⚓︎
Maximum convenience⚓︎
In contrast to end-to-end mode, which places the main focus on security, Masterkey mode provides the maximum level of convenience. It not only imports users, organizational units and roles but also their links and affiliations. It can be synchronized to update the information and affiliations. In this scenario, Active Directory is used as a leading system.
Relevant rights⚓︎
The following options are required to add new profiles.
User right⚓︎
- Can add new Active Directory profiles
- Display organizational structure module
- Display role module
Creating profiles⚓︎
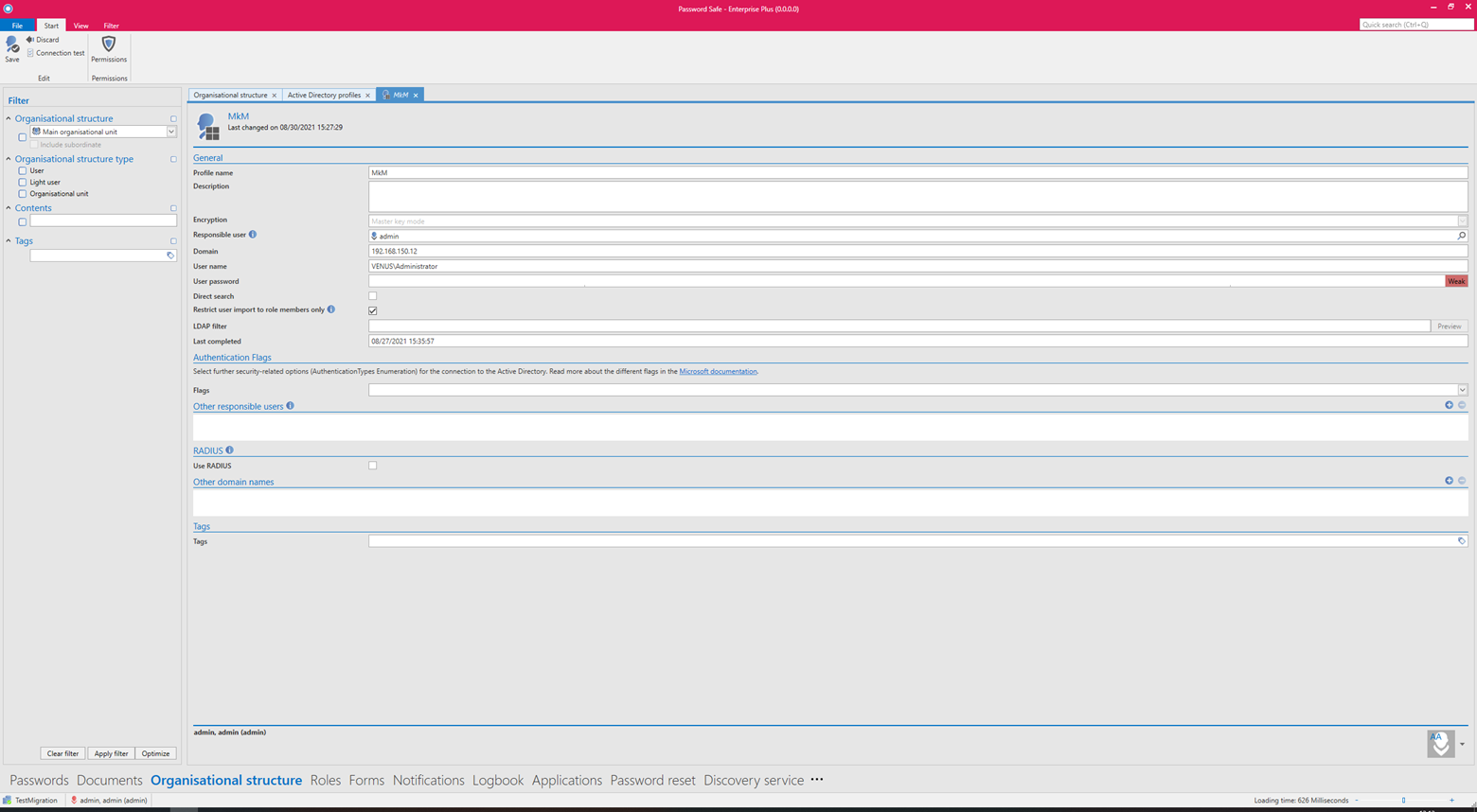
Profile management is started via the icon of the same name on the ribbon.
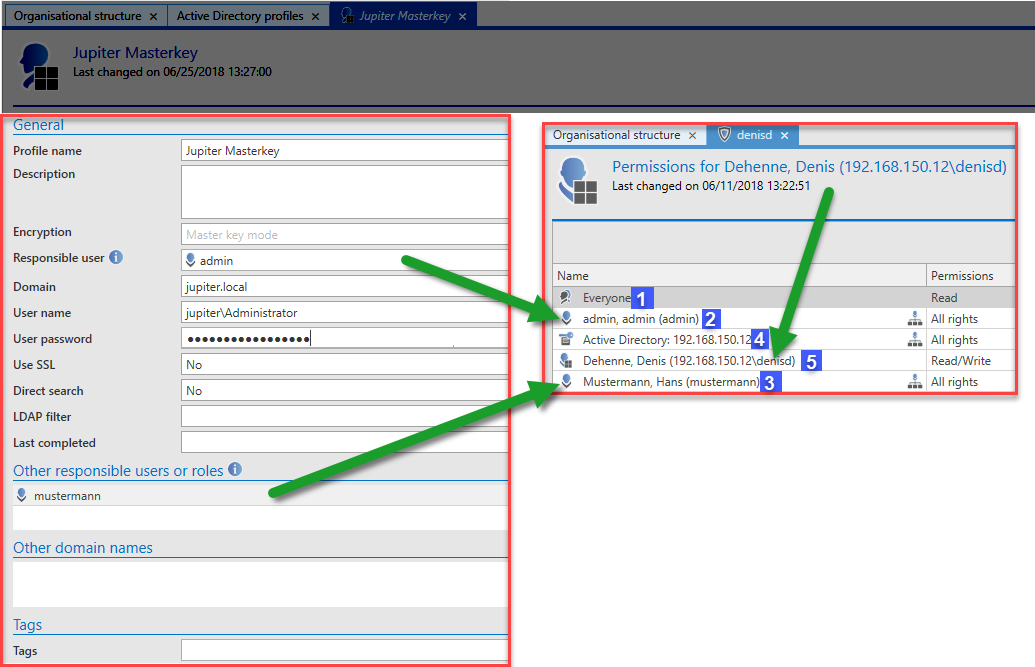
The following information must be provided in the profile:
- Profile name
- An optional description
- Masterkey mode is selected for the encryption
Hint
In the case of already created profiles, the encryption can no longer be changed.
- The domain field is used to define which domain is to be read. The value entered here will also be used for authentication if no alternative spellings have been saved under Other domain names.
- A local user (for example, the administrator) or an already imported user must be specified. The data will be imported under that user’s name.
- A user is required to access the AD. The user should be formatted as follows: Domain\User. It must have access to the AD.
- Corresponding user password (domain password) for the user.
- *Direct search is recommended for very large domain trees. The tree structure is omitted, elements can then only be found and selected via the search.
- By activating the checkbox Restrict user import to role members only, a simplified mode is activated. In this mode, only AD users who are members of at least one role are imported. As soon as they are no longer a member of at least one role, they are deleted from Password Secure.
- By activating the checkbox Force update on next synchronization, ALL records will be updated on the next synchronization, regardless of whether the record has changed in the Active Directory or not. (This checkbox is automatically activated when you have edited the other responsible users and is deactivated again after the next synchronization).
- The LDAP filter can be used to directly specify an AD path as an entry point via an LDAP query.
- Various security options – so-called AuthenticationTypes Enumeration (Flags) – can be selected for the connection of the AD to Password Secure:
- Secure
- SecureSocketsLayer
- ReadOnlyServer
- Signing
- Sealing
Hint
The first two options are already activated by default when configuring a new profile. If a connection is not possible, deactivate SecureSocketsLayer and try again.
- Other responsible users or roles can be used to define who is permitted to carry out the synchronization with the AD.
- The option Other domain names can be used to save alternative spellings of the login domain. These must correspond to the spelling entered in the login window. For example, if a connection is being established to the domain jupiter.local or an IP address, the login can only be carried out with jupiter\user if jupiter has been saved here.
Be Aware
The master key is added in form of a certificate. It is essential to back up the generated certificate! If the database is being moved to another server, the certificate also needs to be transferred! Further information can be found in the section Certificates.
Hint
You can now use the option to integrate a RADIUS server. Read more in the following chapter.
Import⚓︎
You can start the import directly in the ribbon. A wizard guides the user through the entire operation.
Organizational structure⚓︎
First, an organizational unit is selected for the import. If there are no organizational units in the database yet, as in this example, the data is imported into the main organizational unit.
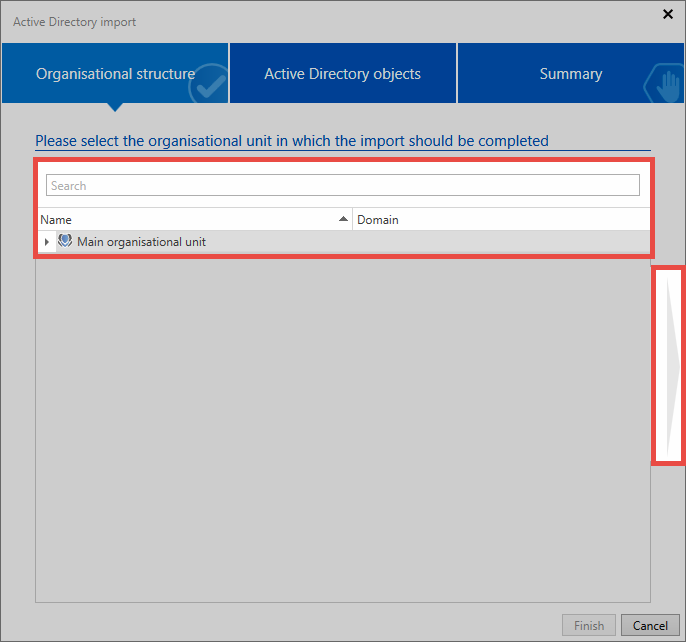
Active Directory objects⚓︎
In the next step, select the profile you will use to import the data. Then, select organizational units and/or users for the import. A search is available for this purpose.
As you can see, the organizational units Jupiter and Contoso contain items to be imported. The organizational units themselves will not be imported. The group 1099 Contractor is imported including all sub-elements. The check next to the group Accounting indicates that the group itself will be imported along with some of its sub-elements. The ticks in the last column ensure that the elements are observed in future synchronization sequences.
There are different symbols which indicate the elements to be imported.
The element itself and all possible sub-elements will be imported The element itself and some of its sub-elements will be imported The element will not be imported; however, it contains elements that will be imported
Right-clicking in the list will launch a context menu. It provides helpful functions for the selection of the individual elements.
Hint
If individual users cannot be selected for import, they have already been imported via an end-to-end encrypted profile.
In the lower area you can specify whether the users just selected for import should be created as Light or Full users.
Summary⚓︎
The last page summarizes which objects will be edited and in what form. It specifies the names of the elements along with their descriptions. The Status column specifies whether the object is added, updated, or disabled. The last column specifies the organizational unit into which the element is imported. The number of objects can be seen at the bottom.
Importing⚓︎
The server imports data in the background. The individual elements then appear in the list one by one. This may take some time, depending on the amount of import data. If the import was terminated, this is symbolized by a hint.
Imported users and organizational units⚓︎
The users and organizational units imported in Masterkey mode cannot be edited in Password Secure. Therefore, any changes must be made in AD and synchronized. AD thus becomes the leading system. Affiliations to roles are also synchronized and must be set in the AD. In organizational units or roles created in Password Secure, the users can be included directly in Password Secure.
Rights⚓︎
The rights will be issued as follows during the import or synchronization.
New objects⚓︎
| User | Groups | Roles | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Are rights inherited from the OU? | If no preset has been saved | If no preset has been saved | No |
| Are rights applied from a preset? | If a preset has been saved | If a preset has been saved | No |
| Is the "add" right issued? | No | Yes | No |
| Who receives the rights key? | Imported users and all with the "authorize" right | All | All with the "authorize" right |
Changed objects⚓︎
| User | Groups | Roles | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Are rights inherited from the OU? | If no preset has been saved | No | No |
| Are rights applied from a preset? | If a preset has been saved | No | No |
| Is the "add" right issued? | No | No | No |
| Who receives the rights key? | All with the "authorize" right | None | All with the "authorize" right |
Hint
If a user is imported, he will be given those roles that he also had in AD insofar as these roles already exist in Password Secure or have also been imported.
Logging into Password Secure⚓︎
Users who are imported using this mode can log in with the domain password. Please note that no domain needs to be specified when logging in. Of course, the login process can also be supplemented with multifactor authentication.
Hint
Logging on using Kerberos works "automatically". As long as the corresponding Kerberos server is accessible, the users in the domain authenticate themselves via Kerberos using their domain password. If the logon via Kerberos does not work – e.g. due to incorrect configuration of the domain controller – the logon via the NTLM protocol is attempted. However, these are all settings that have to be made on the domain controller and have nothing to do with Password Secure.
Be Aware
Logging on to Password Secure using SSO via Kerberos is currently not possible.
Permissions to imported objects⚓︎
The rights to be issued to imported users are explained in the following example:
- In Master Key mode, all users will be issued with the read right.
- The responsible user will be issued with all rights and the key. This ensures that he can also synchronize or change the user in the future
- Other responsible users are issued with the same rights as the responsible user
- The Master Key for the Active Directory profile will also be issued with all rights and keys as it will be used for the synchronization
- Finally, users will be issued with the rights for themselves
Hint
All users and roles issued with rights to the imported object also receive its rights key.
Synchronization⚓︎
During synchronization, all relevant information for users, organizational units and roles (names, email, etc.) is updated. Changed affiliations for roles are adjusted. Likewise, users are activated or deactivated according to the settings in the AD. If the membership of organizational units is to be changed, this can be done by Drag & Drop. New users and correspondingly defined roles are imported.
Hint
If the tick was not set in the Synchronization column when a user is imported, no changes are made.
Manual synchronization⚓︎
The synchronization can be started manually at any time via the corresponding button in the ribbon.
Select the required profile and start the synchronization. As is the case with the initial import, the synchronization runs in the background. A hint indicates that the process has been completed.
Synchronization via system tasks⚓︎
The synchronization can also be carried out automatically. This is made possible via the system tasks.
Deleting or removing users⚓︎
If a user is deleted in Active Directory, it is also deleted in Password Secure during the next synchronization. For this purpose, it is necessary for the user to be imported as a synchronizable user.
If the user is only deleted from Password Secure but retained in Active Directory, a synchronization needs to be carried out to delete it from the database. For this purpose, the wizard is called up via import. The first step is to select an organizational unit. This has no effect when simply deleting a user. The second step is to search for the user. Both ticks are removed.
After checking the summary, the process is concluded. The synchronization is completed and the user is deleted from the database.
Created: 2022-09-05